https://www.gdx.net/product/nutreval-fmv-nutritional-test-blood-urine
A Comprehensive Test for Identifying Functional Nutritional Deficiencies and Insufficiencies
Why Use the NutrEval FMV Profile?
When should testing for NutrEval FMV be considered?
According to the World Health Organization, every country in the world is affected by one or more forms of malnutrition. The term malnutrition addresses 3 broad groups of conditions:1
- Undernutrition (wasting, stunting, underweight)
- Micronutrient-related malnutrition from inadequate or excess vitamins or minerals
- Overweight, obesity, and diet-related noncommunicable diseases (such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes and some cancers)
Proper nutrition is key to preventing a number of diseases. Nutrients are necessary to feed every cell and ensure all body systems are functioning properly. Testing can help clinicians and patients gain an understanding of how nutritional imbalances may be impacting their health. Certain conditions or dietary, genetic, and lifestyle factors may predispose a person to having nutrient imbalances.
Symptoms and conditions associated with nutrient imbalances
- Mood disorders2-6
- Cardiovascular disease7,8
- Obesity/ Insulin resistance/ Type 2 Diabetes9-12
- Autism13-16
- Fatigue17-20
- Weight Issues/ Malnutrition/ Dietary Guidance
- Maldigestion/Malabsorption
- Increased nutrient demand in physical trauma/healing21
The NutrEval FMV Biomarkers
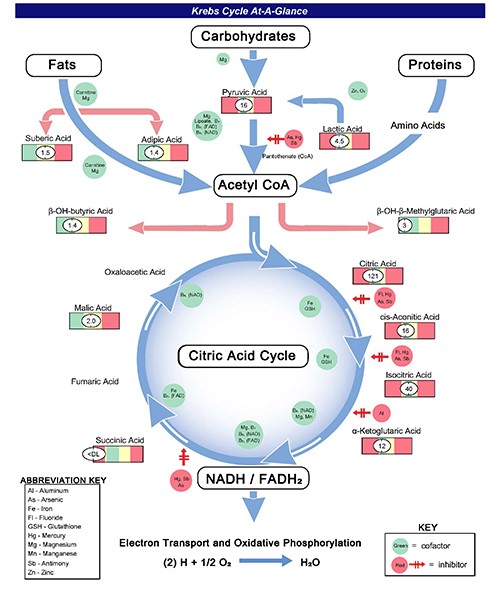
- Metabolic Analysis Markers (urine organic acids)
- Malabsorption and Bacterial/ Yeast Dysbiosis Markers are metabolites produced by the gastrointestinal microbiome
- Cellular Energy & Mitochondrial Metabolites are biomarkers of carbohydrate and fatty acid metabolism, and the citric acid (Kreb’s) cycle
- Neurotransmitter Metabolites are downstream byproducts of epinephrine, norepinephrine, serotonin and dopamine
- Vitamin Marker are specific analytes used to assess functional levels of vitamin cofactors
- Toxin & Detoxification Markers relate to certain toxic metabolites and the body’s detoxification capacity
- Amino Acids (urine)
- Essential Amino Acids must be derived from dietary sources
- Nonessential Amino Acids are synthesized by the body
- Intermediary Metabolites are byproducts of amino acid metabolism
- B Vitamin Markers are involved in biochemical reactions that specifically require B vitamins
- Urea Cycle Markers are byproducts associated with nitrogen detoxification
- Glycine/Serine Metabolites are involved in the choline to acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) pathway and the methylation pathways
- Dietary Peptide Related Markers can indicate incomplete protein breakdown
- Essential and Metabolic Fatty Acids Markers (RBCs)
- Omega 3 Fatty Acids are essential for brain function and cardiovascular health and are anti-inflammatory
- Omega 6 Fatty Acids are involved in the balance of inflammation
- Omega 9 Fatty Acids are important for brain growth, nerve cell myelin, and reducing inflammation
- Saturated Fatty Acids are involved in liproprotein metabolism and adipose tissue inflammation
- Monounsaturated Fats include omega 7 fats and unhealthy trans fats
- Delta-6 Desaturase Activity assesses efficiency of this enzyme to metabolize omega 6’s and omega 3’s
- Cardiovascular Risk includes specific ratios and the Omega 3 Index
- Oxidative Stress Markers include antioxidants glutathione (whole blood) and Coenzyme Q10 (serum), as well as the oxidative damage markers lipid peroxides and 8-OHdG (urine)
- Vitamin D (serum) measures a total of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 (ergocalciferol)
- Elemental Markers
- Nutrient Elements are direct measurements of copper and zinc (plasma), magnesium and potassium (RBC), and manganese and selenium (whole blood)
- Toxic Elements (whole blood) indicate exposure to lead, mercury, arsenic, cadmium or tin within approximately a 90-120 day timeframe
- Add-on SNPs (buccal swab) include MTHFR, COMT, TNF-a, and APOE


